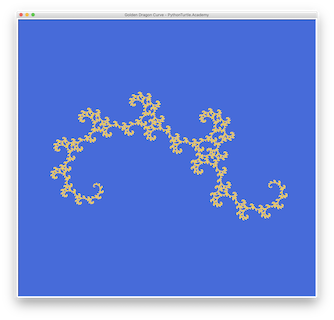
Draw a dragon curve based on the golden ratio. At each recursion, the first recursion step turns 32.89 degrees to the left and move 0.74 times the original distance; the second recursion step turns 46.99 degrees to the right and move 0.55 times the original distance. Please check out this web page on mathematical details of the golden dragon.
The following show the recursions depths from 0 to 3.




The following figure is generated not by the recursion depth but by stopping the recursion when the distance becomes smaller than 1.

Source Code:
import turtle
import math
screen = turtle.Screen()
screen.title('Golden Dragon Curve - PythonTurtle.Academy')
screen.setup(1000,1000)
screen.setworldcoordinates(-1000,-1000,1000,1000)
turtle.speed(0)
turtle.hideturtle()
turtle.pencolor('gold')
screen.bgcolor('royal blue')
screen.tracer(0,0)
golden_ratio = (1+5**0.5)/2
r1 = r = (1/golden_ratio)**(1/golden_ratio)
r2 = r1**2
angle1 = math.acos((1+r**2-r**4)/(2*r))
angle2 = math.acos((1+r**4-r**2)/(2*r**2))
print(r1,r2,math.degrees(angle1),math.degrees(angle2))
def golden_dragon(x1,y1,x2,y2,turn,n):
dist = ((x2-x1)**2 + (y2-y1)**2)**0.5
if dist<1:
turtle.goto(x2,y2)
return
angle = math.atan2(y2-y1,x2-x1)
if turn:
px = x1+dist*r1*math.cos(angle+angle1)
py = y1+dist*r1*math.sin(angle+angle1)
else:
px = x1+dist*r2*math.cos(angle-angle2)
py = y1+dist*r2*math.sin(angle-angle2)
golden_dragon(x1,y1,px,py,True,n-1)
golden_dragon(px,py,x2,y2,False,n-1)
turtle.up()
turtle.goto(-500,-200)
turtle.down()
golden_dragon(-500,-200,700,-200,True,3)
screen.update()