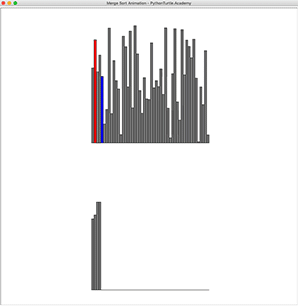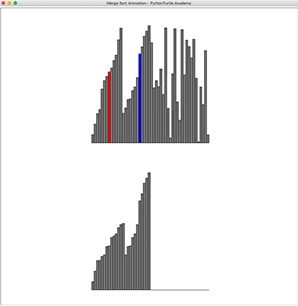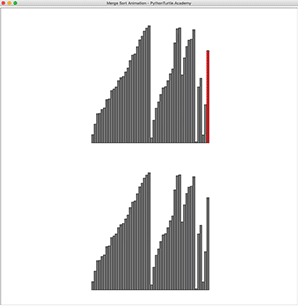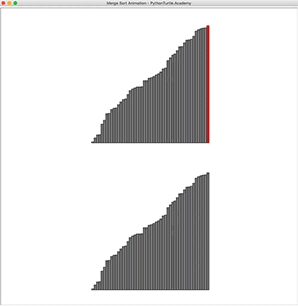
In previous sorting animations, we animated selection, insertion, and bubble sort. They are slow O(n^2) slow sorting algorithm. Merge Sort, a divide and conquer algorithm, is a much faster sorting algorithm with the worst case running time of O(n*logn). However, unlike previous sorting algorithms, it requires another array to be able to merge. Implement Merge Sorting and animate it!
Here is the source code:
import turtle
import random
import time
screen = turtle.Screen()
screen.setup(1000,1000)
screen.setworldcoordinates(-1000,-1000,1000,1000)
screen.tracer(0,0)
screen.title('Merge Sort Animation - PythonTurtle.Academy')
turtle.speed(0)
turtle.hideturtle()
def draw_bar(x,y,w,h):
turtle.up()
turtle.goto(x,y)
turtle.seth(0)
turtle.down()
turtle.begin_fill()
turtle.fd(w)
turtle.left(90)
turtle.fd(h)
turtle.left(90)
turtle.fd(w)
turtle.left(90)
turtle.fd(h)
turtle.left(90)
turtle.end_fill()
def draw_bars(v,w,n,currenti=-1,currentj=-1):
turtle.clear()
x = -400
wd = 800/n
for i in range(n):
if i == currenti: turtle.fillcolor('red')
elif i == currentj: turtle.fillcolor('blue')
else: turtle.fillcolor('gray')
draw_bar(x,100,wd,v[i])
x += wd
x = -400
for i in range(n):
turtle.fillcolor('gray')
draw_bar(x,-900,wd,w[i])
x += wd
screen.update()
def merge(v,w,a,b,x,y):
i,j, k = a,x,a
while i<=b and j<=y:
if v[i] < v[j]: w[k],i = v[i], i+1
else: w[k], j = v[j], j+1
draw_bars(v,w,n,i,j)
k += 1
while i<=b:
w[k],i,k = v[i],i+1,k+1
draw_bars(v,w,n,i,j)
while j<=y:
w[k],j,k = v[j],j+1,k+1
draw_bars(v,w,n,i,j)
for i in range(a,y+1):
v[i] = w[i]
draw_bars(v,w,n,i)
def merge_sort(v,w,x,y):
if x >= y:
return
m = (x+y)//2
merge_sort(v,w,x,m)
merge_sort(v,w,m+1,y)
merge(v,w,x,m,m+1,y)
n = 50
v = [0] * n
w = [0] * n
for i in range(n):
v[i] = random.randint(1,800)
t1 = time.time()
merge_sort(v,w,0,n-1)
t2 = time.time()
print('elapsed time=', t2-t1)
What’s Next?